Emergency trips are vital for safeguarding the engine in fault or abnormal running conditions & are the last line of defense. Emergency trip/shutdown will be triggered for following cases:
- Overspeed –if engine speed is above 110% of the rated speed
- High density of oil mist in the crankcase
- Low L.O. pressure (usual setting is 3.5 bar)
- High H.T. cooling water outlet temp(usual setting is 95°C)
- Failure of both speed measuring sensors –
There are two independent speed measuring sensors(pick-ups).One for the Control system & the other for the Safety system.If both of them fail,engine will trip.
How Emergency Shutdown Takes Place
Engine emergency shutdown or trip is executed by two independent mechanisms.Two means are provided for redundancy purpose,to ensure tripping of the engine still takes place,even,when one of systems fails.
1.Shutdown by Governor–the governor link shifts the fuel control shaft to “zero index”,as result all fuel pump racks are set to zero and fuel supply to the engine is completely cut-off.
2. Shut down by Emergency stop cylinder.
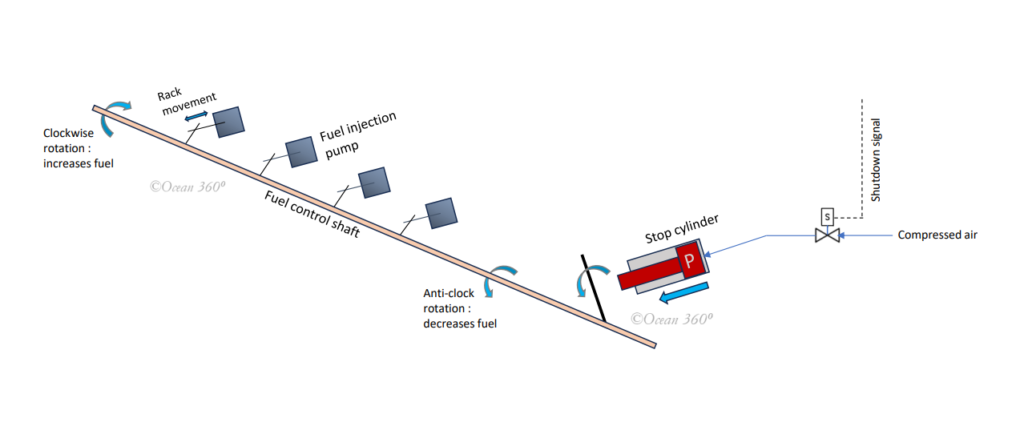
Figure 1 Emergency shutdown by stop cylinder
Ref. to the figure 1 above.
Whenever trip signal is initiated by the safety system,solenoid valve(S) is energized & opened.Compressed air enters into the emergency stop cylinder & pushes the piston(P) in the direction indicated.This in turn pushes the adjoining bar (B) connected to the fuel control shaft.
Fuel control shaft is rotated fully anti-clockwise and all fuel injection pumps racks are pushed outward to zero index.Engine stops due to starvation of fuel oil.